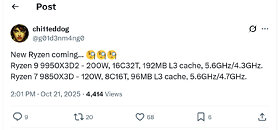
Server DRAM Pricing Jumps 50%, Only 70% of Orders Getting Filled
Server memory has become the scarcest commodity in tech. According to DigiTimes, Samsung and SK Hynix quietly circulated fourth-quarter contract appendix that retroactively increased RDIMM prices by 40-50%. Even hyperscalers that signed agreements in August must now pay the new rate or risk losing their queue position. The two Korean manufacturers simultaneously reduced confirmed allocations by 30%, pushing Tier-1 U.S. and Chinese cloud order books to an effective 70% fill rate and eliminating the safety stock most buyers believed they had secured. Module manufacturers such as Kingston and ADATA now pay $13 for 16 GB DDR5 chips that cost $7 six weeks ago, an increase large enough to erase entire gross margin.
Smaller OEMs and channel distributors have been told to expect 35-40% fulfillment through the first quarter of 2026, forcing them either to gamble on the spot market or idle production lines. Even the older DDR4, now reduced to 20% of global DRAM output, is affected. Switches, routers, and set-top boxes that still use DDR4 are suddenly facing very long lead times because no fabrication plant wants to allocate wafers to trailing nodes. Analysts at TrendForce now forecast that the DRAM shortfall will outlast the 2026 hyperscaler build-out, meaning the industry's next relief valve may not be new capacity but a potential demand contraction, an outcome no manufacturer is willing to budget for.
Smaller OEMs and channel distributors have been told to expect 35-40% fulfillment through the first quarter of 2026, forcing them either to gamble on the spot market or idle production lines. Even the older DDR4, now reduced to 20% of global DRAM output, is affected. Switches, routers, and set-top boxes that still use DDR4 are suddenly facing very long lead times because no fabrication plant wants to allocate wafers to trailing nodes. Analysts at TrendForce now forecast that the DRAM shortfall will outlast the 2026 hyperscaler build-out, meaning the industry's next relief valve may not be new capacity but a potential demand contraction, an outcome no manufacturer is willing to budget for.